Data Science vs Data Engineering: Key Differences You Must Know
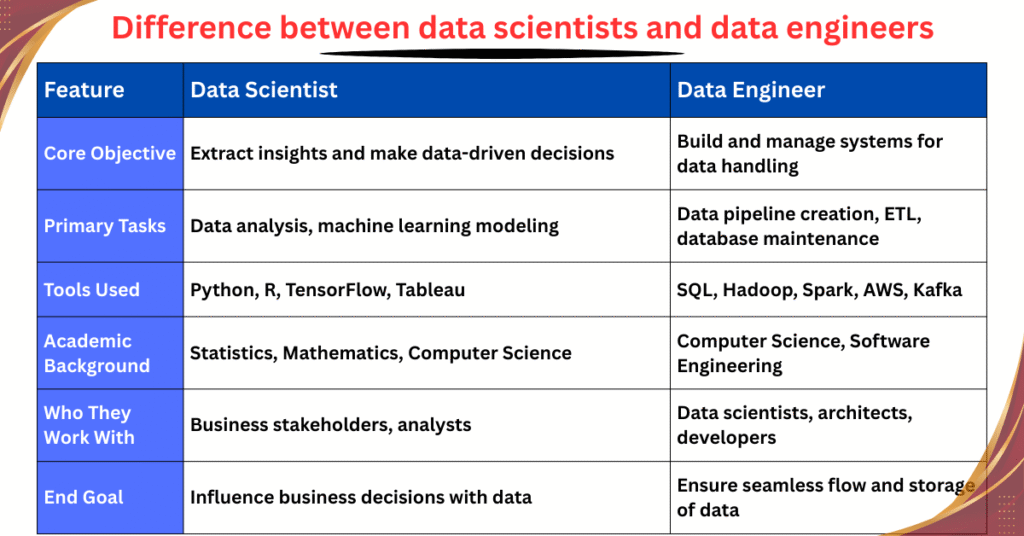
In today’s digital landscape, businesses heavily rely on data to drive growth, innovation, and strategic decisions. Two crucial roles making this possible are data scientists and data engineers. While they often work closely together, the focus, skill sets, and goals of each profession are quite distinct.
If you’re exploring a career in data science or data engineering, or just trying to understand how these roles contribute to modern businesses, this guide will help you grasp the major differences and decide which path suits you best.
What is Data Science?
Data science is a field dedicated to extracting knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. Using statistical techniques, machine learning, and advanced analytics, data scientists solve complex business problems and predict future outcomes.
Main Responsibilities of a Data Scientist
-
Data Exploration: Examining and understanding the structure and patterns within data.
-
Predictive Modeling: Building machine learning models to forecast trends and behaviors.
-
Data Visualization: Creating charts and dashboards to present data in a clear and actionable way.
-
Statistical Testing: Validating hypotheses and drawing conclusions from datasets.
-
Business Communication: Turning technical findings into strategic recommendations for stakeholders.
Essential Skills for a Data Scientist
-
Programming: Expertise in Python, R, and SQL is vital.
-
Statistical Knowledge: Strong foundation in probability, statistical testing, and data distributions.
-
Machine Learning: Familiarity with algorithms, deep learning, and tools like TensorFlow or scikit-learn.
-
Visualization Tools: Using platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, or Matplotlib.
-
Big Data Handling: Basic understanding of technologies like Hadoop and Spark.
What is Data Engineering?
While data science focuses on analyzing and interpreting data, data engineering is about building the infrastructure that makes this data usable. Data engineers create systems to collect, clean, transform, and store data so that analysts and scientists can access reliable datasets easily.
Key Responsibilities of a Data Engineer
-
Building Data Pipelines: Automating data movement between systems.
-
ETL Operations: Extracting data from sources, transforming it into usable formats, and loading it into storage systems.
-
Database Management: Designing and maintaining efficient, scalable databases and warehouses.
-
Integrating Data Sources: Combining diverse data from APIs, servers, and cloud storage into unified systems.
-
Optimizing Systems: Enhancing performance, scalability, and reliability of data flows.
Required Skills for Data Engineers
-
Coding Skills: Proficiency in SQL, Python, Java, or Scala.
-
Big Data Tools: Knowledge of Apache Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka.
-
Database Expertise: Working with SQL and NoSQL databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, or Cassandra.
-
Cloud Technology: Experience with AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud data services.
-
ETL and Workflow Tools: Familiarity with Apache Airflow, Talend, or AWS Glue.
How Data Scientists and Data Engineers Work Together
In practice, data engineers and data scientists collaborate constantly. A data engineer ensures that data is accessible, organized, and stored securely. Without this foundation, data scientists would struggle to find clean, accurate data to build models or draw insights.
Similarly, data scientists provide feedback about the quality and format of data, helping engineers refine and improve the pipelines and storage solutions. This collaboration is key to successful data-driven strategies.
Career Opportunities in Data Science and Data Engineering
Both fields offer strong career prospects, but the paths differ in terms of focus and growth potential.
Career in Data Science
-
Entry-Level Data Scientist: Cleans data, assists in analysis, builds basic models.
-
Mid-Level Data Scientist: Designs machine learning models and handles complex datasets.
-
Senior Data Scientist: Leads modeling projects, mentors teams, and drives data strategies.
-
Chief Data Scientist or Head of Analytics: Oversees organizational data strategies and innovation.
Data science career opportunities are plentiful across sectors like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and technology, where predictive modeling and analytics are mission-critical.
Career in Data Engineering
-
Junior Data Engineer: Supports ETL processes and builds simple data pipelines.
-
Data Engineer: Designs, tests, and optimizes complex systems.
-
Senior Data Engineer: Leads system architecture improvements and manages data flow strategies.
-
Data Architect: Plans and builds enterprise-wide data management frameworks.
Demand for data engineering careers is booming as companies handle increasing volumes of data and seek scalable, secure infrastructures.
Which Path Should You Choose?
Choosing between a career in data science vs data engineering depends largely on your interests and strengths:
-
Choose data science if you love digging into patterns, building models, making predictions, and influencing strategic business decisions through data insights.
-
Opt for data engineering if you enjoy building and optimizing systems, solving technical challenges, and ensuring that data flows efficiently and securely.
Both roles require logical thinking, coding skills, and a deep understanding of data — but their day-to-day work is very different.
Final Thoughts: Data Science vs Data Engineering
Understanding the difference between data science and data engineering is essential whether you’re planning your career or assembling a data team for your organization.
-
Data scientists turn raw data into actionable insights, driving smarter decisions.
-
Data engineers build the platforms and tools that make all this analysis possible.
Both roles are equally important in today’s data-powered economy. Choosing one over the other isn’t about which is “better,” but about what fits your passion, skills, and long-term goals.
If you’re stepping into the world of big data, mastering the right skills — whether it’s data engineering responsibilities or skills for data scientists — will set you on the path to success.
FAQs:
1. What is the main difference between data science and data engineering?
Answer:
The main difference is that data scientists analyze and interpret complex data to find patterns and insights, while data engineers design and build systems to collect, store, and manage that data efficiently. Simply put, engineers prepare the data, and scientists analyze it.
2. Who earns more: data scientist or data engineer?
Answer:
Salaries can vary by location and experience, but generally, data scientists tend to earn slightly more due to the demand for advanced machine learning and statistical skills. However, with cloud and big data expertise, senior data engineers can also command very high salaries.
3. Should I become a data scientist or a data engineer?
Answer:
Choose data science if you enjoy analyzing data, building models, and deriving insights. Choose data engineering if you prefer coding, building systems, and handling large-scale data infrastructure. Both careers are in high demand and offer strong growth potential.
4. Can a data engineer become a data scientist?
Answer:
Yes, a data engineer can transition to a data scientist role by learning machine learning algorithms, statistics, and data analysis techniques. Since engineers already understand data structures and programming, they have a solid foundation to build upon.
5. Is data engineering harder than data science?
Answer:
Both fields have their own challenges. Data engineering requires deep technical knowledge of databases, cloud platforms, and data architecture, while data science demands strong analytical skills, statistical knowledge, and machine learning expertise. The difficulty depends on your personal strengths and interests.

Cybersecurity Architect | Cloud-Native Defense | AI/ML Security | DevSecOps
With over 23 years of experience in cybersecurity, I specialize in building resilient, zero-trust digital ecosystems across multi-cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP) and Kubernetes (EKS, AKS, GKE) environments. My journey began in network security—firewalls, IDS/IPS—and expanded into Linux/Windows hardening, IAM, and DevSecOps automation using Terraform, GitLab CI/CD, and policy-as-code tools like OPA and Checkov.
Today, my focus is on securing AI/ML adoption through MLSecOps, protecting models from adversarial attacks with tools like Robust Intelligence and Microsoft Counterfit. I integrate AISecOps for threat detection (Darktrace, Microsoft Security Copilot) and automate incident response with forensics-driven workflows (Elastic SIEM, TheHive).
Whether it’s hardening cloud-native stacks, embedding security into CI/CD pipelines, or safeguarding AI systems, I bridge the gap between security and innovation—ensuring defense scales with speed.
Let’s connect and discuss the future of secure, intelligent infrastructure.